Methods of purification
Pure substances:
A pure substance contain only one type of substance i.e only one type of atoms or molecules.
There are certain methods to check the purity of any substance.
1- Checking its melting point.
2- checking its boiling point.
3- testing it by chromatography.
If any impurity is present it lowers the melting point , higher the boiling point ( it will melt or boil at range of temperature rather than a fixed point) and it will give more than one spots on chromatogram.
There also certain methods of purification of matter which are as follows:
1- dissolving, filtering and evaporating.
2- decanting and centrifuging.
3- separating funnel.
4- sublimation.
5- distillation.
6- chromatography.
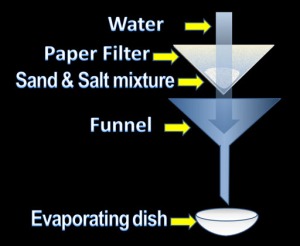
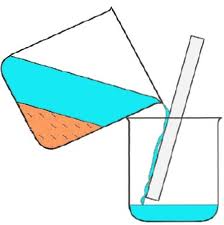
1- Dissolving, filtering and evaporating:
This technique is only suitable for separating a mixture of solids which behave differently in a particular solvent and one of them should must be soluble in the solvent and other shouldn’t.
At first the mixture of such solids are dissolved in a solvent by stirring and then filtered using a filter paper the solvent along with the soluble solid passes through the paper as filtrate where as the insoluble one remains on the paper as residue. One of the example of this process is separating a solution of salt and sand.
The soluble solid can then be separated from the solvent by process of evaporation better known as crystallisation.
2-Decanting and centrifuging:
These process are used to separate fine insoluble particles from a liquid e.g chalk particles suspended in water.
In decanting they are allowed to settle down first and the carefully water is poured into another container but usually not very effective.
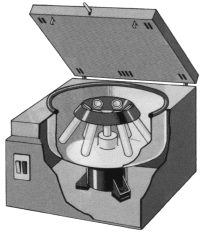
 In centrifuging a machine is used to separate suspended particles, The machine rotates at a very high speed and the particles settle at the bottom of the tube .The structure of machine is shown below.
In centrifuging a machine is used to separate suspended particles, The machine rotates at a very high speed and the particles settle at the bottom of the tube .The structure of machine is shown below.
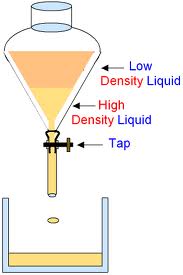
3- Separating Funnel:
Separating funnel is used to separated such liquid which are not miscible or immiscible such as oil and water they do not mix together.Such liquids are closed in a separating funnel and the heavier liquid is allowed to come at the bottom then the tap is opened and the liquids are collected in separate containers however this is not very effective method of purification.
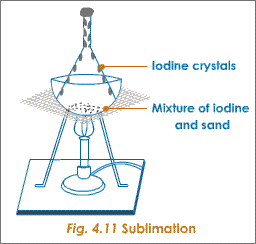
4- Sublimation:
This technique is used only to separate or purify such solids which changes directly to gas on heating e.g iodine hence it has a limited in use.
Sublimation is a property of covalent compounds e.g ammonium chloride.
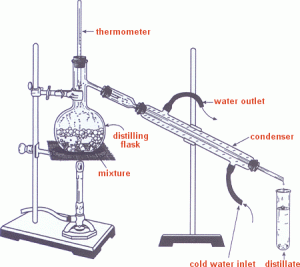
5- Distillation:
This process is used to obtain a pure liquid and concentrated solution or a solid solute from a solution e.g a solution of salt and water.
as shown in the figure the mixture is heated so that the liquid can be turned into vapours. These vapours then passes through a condenser so that a liquid (distillate) can be obtained. Some time some anti bumping granules are added in the boiling flask to prevent the vigorous formation of bubbles.
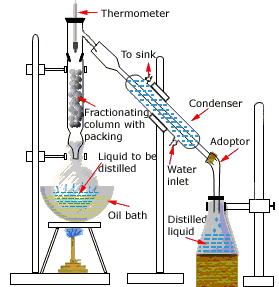
There is an other type of distillation which is in fact of more practical use.
It is known as Fractional distillation.
This type of distillation is used to separate miscible liquids e.g alcohol and water it depends upon different boiling points of fractions present in the solution e.g alcohol ha 78 Celsius and water has 100 Celsius
It has a same procedure as simple distillation it only has a additional fractionating column which help to prevent the escape of vapours of liquid with higher boiling point at lower temperature.
This technique is used in purification of crude oil , alchol and gases from liquid air.
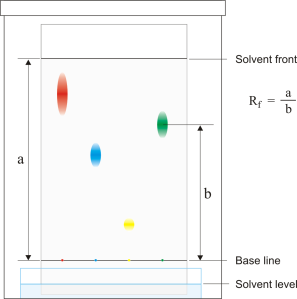
6- Chromatography:
This technique is used to separate dyes and pigments from a colour solution or mixture. In this process the key factor is the solubility of pigments in the solvent used usually organic solvents like alcohol are used.
Rate of Flow: is the ratio of distance covered by the the dye and the distance covered by solvent.
Some there are some substances which do not give a spot on the chromatograph e.g amino acids in such cases a locating agent is used to detect the spots.